NASA is the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. They do amazing things like sending rockets to space and exploring Mars. In this article, you will learn about NASA’s famous space missions like the Apollo Program and Mars rovers. Also, see how NASA works with other countries on the International Space Station and how they create new technology. We will talk about their future goals, like going back to the Moon and planning trips to Mars. Let’s dive into NASA’s exciting work and see how they are exploring space.
Introduction to NASA

NASA, or the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, is at the forefront of space exploration and technological innovation. Founded in 1958, NASA was established to lead the nation’s efforts in space science and technology. Over the decades, it has accomplished groundbreaking feats, from landing humans on the Moon to deploying sophisticated telescopes that peer deep into the cosmos. Understanding NASA’s impact helps us appreciate its crucial role in advancing our knowledge of space.
Major NASA Space Missions
Apollo Program
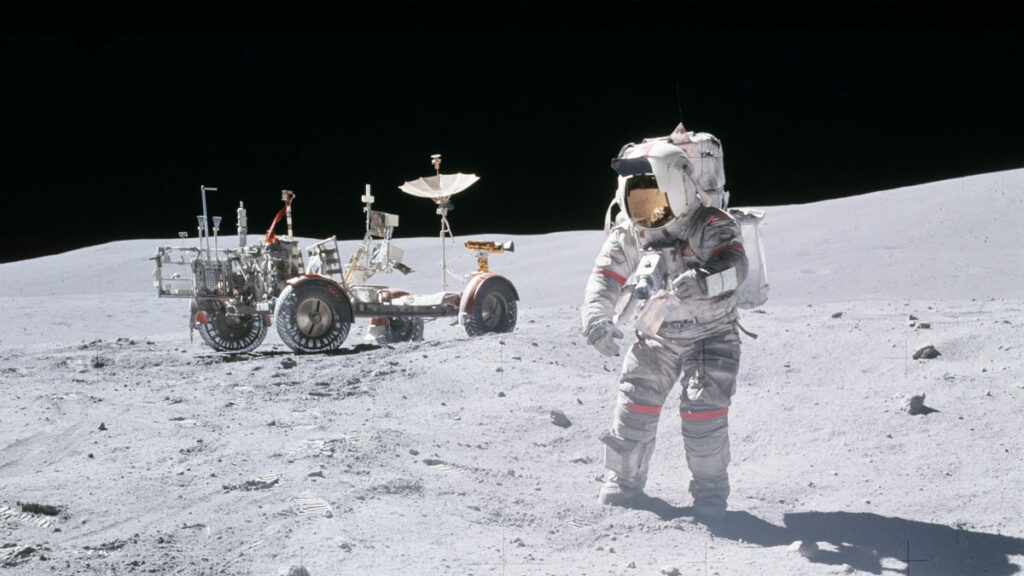
One of NASA’s most celebrated achievements is the Apollo Program. Launched in the 1960s, this series of missions aimed to land humans on the Moon and safely return them to Earth. The most iconic mission, Apollo 11, saw astronauts Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin make history as the first humans to walk on the lunar surface. These missions not only demonstrated technological prowess but also marked a significant milestone in human exploration.
Mars Rover Missions

Another pivotal aspect of NASA’s exploration efforts is its Mars Rover Missions. The Curiosity and Perseverance rovers have provided invaluable insights into the Martian surface, searching for signs of past life and assessing the planet’s habitability. These rovers are equipped with advanced scientific instruments, enabling them to conduct experiments and relay data back to Earth, enhancing our understanding of the Red Planet.
Voyager Probes
The Voyager Probes are another testament to NASA’s enduring legacy. Launched in 1977, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 have traveled beyond our solar system, sending back data about the outer reaches of space. These probes have expanded our knowledge of the heliosphere and interstellar space, marking significant achievements in space exploration.
NASA’s Role in International Collaboration
International Space Station (ISS)
NASA plays a central role in the International Space Station (ISS), a collaborative project involving space agencies from around the world, including ESA (European Space Agency), JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and Roscosmos. The ISS serves as a microgravity laboratory where scientific research and technological experiments are conducted, fostering international cooperation and advancing space science.
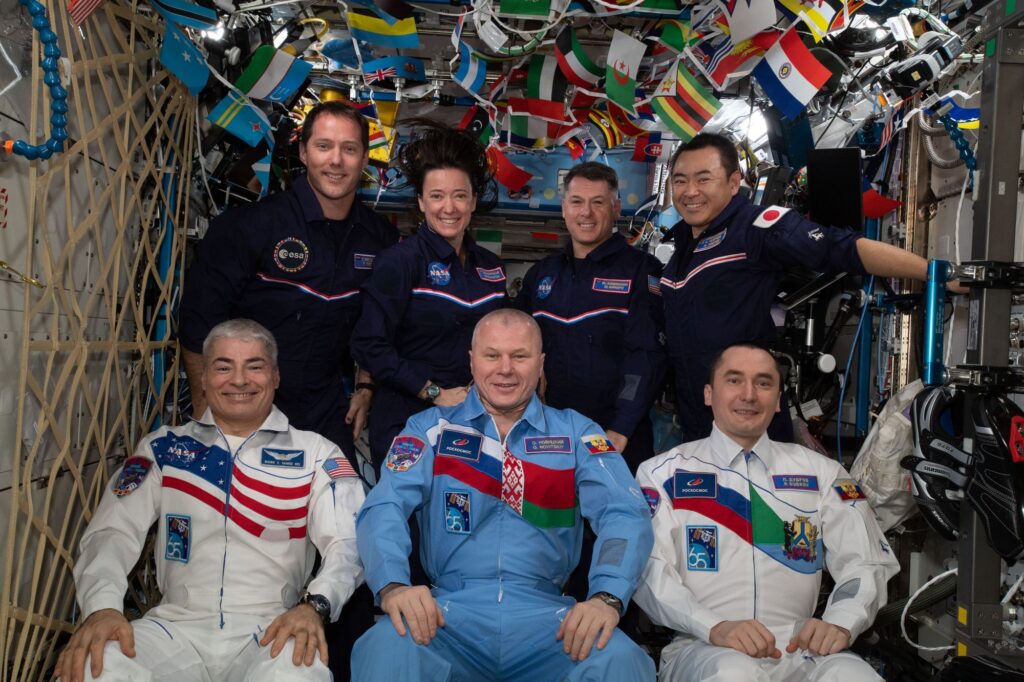

Global Partnerships
NASA’s partnerships extend beyond the ISS. Collaborations with other space agencies and private companies, such as SpaceX, enhance our capabilities and expand the scope of space missions. These alliances enable the sharing of technology, expertise, and resources, accelerating progress in space exploration.
Technological Innovations by NASA
Space Shuttle Program
The Space Shuttle Program, which ran from 1981 to 2011, was a major milestone in space travel. This reusable spacecraft enabled frequent missions to low Earth orbit, including satellite deployments and scientific experiments. The program’s innovations paved the way for the development of more advanced space technologies.
Spacecraft and Satellites
NASA has developed numerous spacecraft and satellites that have revolutionized our understanding of the universe. Notable examples include the Hubble Space Telescope, which has provided stunning images and valuable data about distant galaxies, and the James Webb Space Telescope, set to further deepen our understanding of the cosmos.
NASA’s Contributions to Science and Research
Astronomical Research
NASA’s astronomical research has led to numerous discoveries, from the nature of black holes to the formation of distant galaxies. Instruments like the Hubble and Webb telescopes have allowed scientists to observe the universe in unprecedented detail, advancing our knowledge of cosmic phenomena.
Space Science
In addition to astronomical research, NASA’s contributions to space science include studies on cosmic radiation, planetary geology, and the search for extraterrestrial life. These efforts enhance our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
NASA’s Astronaut Training and Space Travel
Training Programs
NASA’s astronaut training programs are rigorous and comprehensive. They include physical fitness, technical skills, and simulated space missions to prepare astronauts for the challenges of space travel. Training facilities like the Johnson Space Center play a critical role in this preparation.
Human Spaceflight
NASA’s human spaceflight missions have been pivotal in exploring space. From the historic Apollo moon landings to the recent missions aboard the ISS, human spaceflight continues to push the boundaries of what is possible.
Future Goals and Projects of NASA
Lunar Exploration
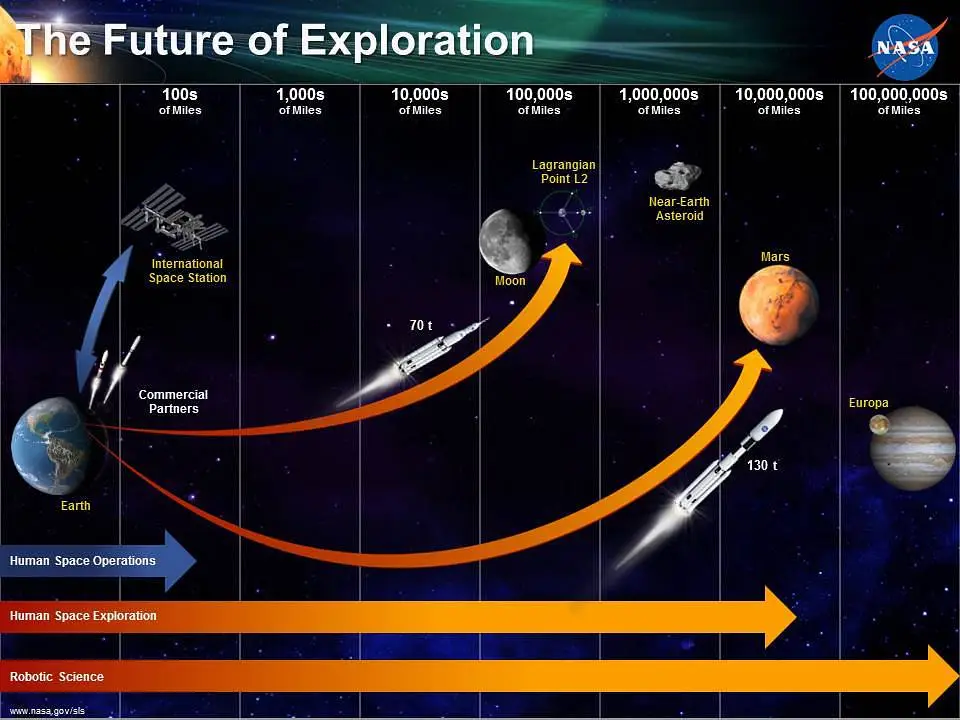
Looking ahead, NASA’s Lunar Exploration plans are ambitious. The Artemis Program aims to return humans to the Moon and establish a sustainable presence, paving the way for future exploration of Mars. These missions will test new technologies and expand our capabilities in deep space.
Mars Exploration
Mars remains a key focus for NASA. Plans for human missions to Mars are underway, with research and technology development aimed at making this ambitious goal a reality. The insights gained from Mars exploration could revolutionize our understanding of planetary science and the potential for life beyond Earth.

NASA’s Impact on Space Policy and Public Awareness
Space Policy and Advocacy
NASA plays a significant role in shaping space policy. By collaborating with governmental bodies and international organizations, NASA helps set the direction for space exploration and policy, influencing how space is explored and utilized.
Public Engagement
Engaging the public is another crucial aspect of NASA’s work. Through educational programs, outreach activities, and media communications, NASA fosters public interest in space exploration and scientific discovery. These efforts help inspire future generations of scientists, engineers, and space enthusiasts.
Conclusion
NASA’s achievements in space exploration, from lunar landings to Mars missions, showcase their incredible impact on science and technology. For more insights into NASA’s work and space exploration, visit us at Galaxy Secrets. We invite you to leave comments, share your thoughts, and explore more of our content. Join us in celebrating the wonders of space!
FAQs About NASA
What are NASA’s most significant space missions?
NASA has been behind several major space missions that have reshaped our understanding of the universe. Among the most significant are the Apollo Program, which landed the first humans on the Moon, and the Mars Rover missions like Curiosity and Perseverance, which explored the Martian surface. Additionally, the Voyager Probes have traveled beyond our solar system, providing valuable data about the outer reaches of space.
How does NASA collaborate with international space agencies?
NASA collaborates extensively with international space agencies to advance space exploration. One of the most notable examples is the International Space Station (ISS), a joint project involving NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency), and Roscosmos. These collaborations facilitate shared missions, technological development, and scientific research.
What are some of NASA’s technological innovations?
NASA is known for its technological advancements that push the boundaries of space exploration. Key innovations include the Space Shuttle Program, which revolutionized space travel with reusable spacecraft, and advanced spacecraft and satellites like the Hubble Space Telescope and the James Webb Space Telescope, which have provided unprecedented views of the universe.








