Jupiter, the largest planet in our Solar System, is a gas giant that captivates astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. Its immense size, dynamic atmosphere, and intriguing moons make it a fascinating subject of study. Let’s dive into the fundamental aspects of this colossal planet.
Jupiter’s Size and Mass
Jupiter is truly a giant among planets. With a diameter of 142,984 km and a mass of 1.898 × 10^27 kg, it outweighs all other planets combined. This incredible mass gives Jupiter a strong gravitational pull, influencing the orbits of many objects within the Solar System.

Composition of Jupiter’s Atmosphere
The atmosphere of Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. These gases create a thick, swirling atmosphere, with ammonia clouds giving it a distinctive striped appearance. This dynamic environment is home to many storms, including the infamous Great Red Spot.
Jupiter’s Magnetic Field
One of the most remarkable features of Jupiter is its powerful magnetic field, which is 14 times stronger than Earth’s. This field creates intense radiation belts and spectacular auroras at the planet’s poles. Understanding this magnetic field helps scientists learn more about the planet’s internal structure.
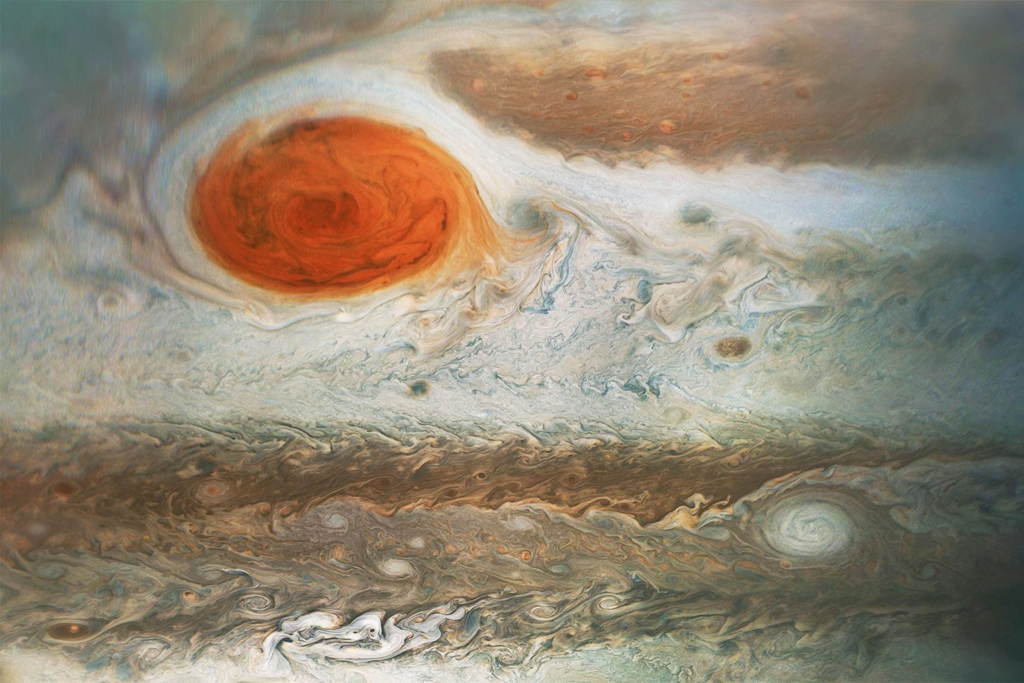
Great Red Spot and Other Storms
The Great Red Spot is perhaps Jupiter’s most famous feature. This gigantic storm, which has raged for centuries, is larger than Earth and showcases the planet’s volatile weather. Besides the Great Red Spot, Jupiter’s atmosphere hosts numerous other storms and turbulence, each contributing to its complex climate.

Exploring Jupiter’s Moons
Jupiter is accompanied by a diverse group of moons, each with unique characteristics. The four largest moons—Europa, Ganymede, Io, and Callisto—are known as the Galilean moons.
Overview of Jupiter’s Moons
Jupiter has 79 known moons, but the Galilean moons are the most significant. Discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610, these moons offer a glimpse into the variety of celestial bodies orbiting the giant planet.
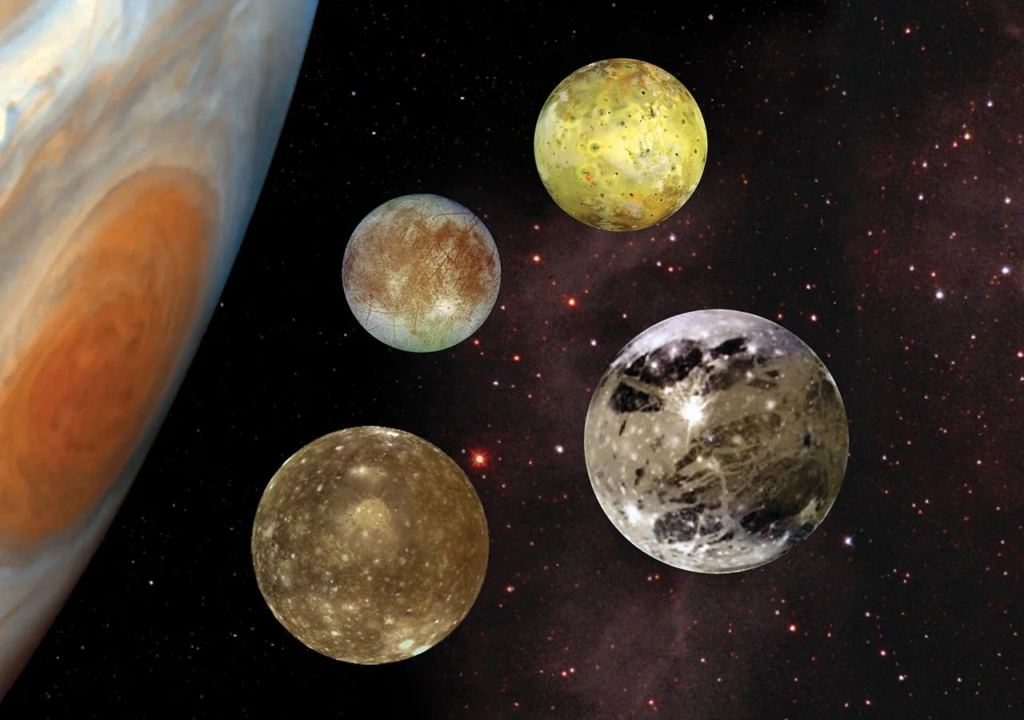

Major Moons: Europa, Ganymede, Io, and Callisto
- Europa: Known for its icy surface and the potential for an ocean beneath. Scientists believe that Europa may harbor conditions suitable for life.
- Ganymede: The largest moon in the Solar System, Ganymede even surpasses Mercury in size. It has its own magnetic field.
- Io: The most volcanically active body in the Solar System, with hundreds of volcanoes dotting its surface.
- Callisto: Heavily cratered and ancient, Callisto’s surface tells the story of a long and tumultuous history.
Geological Features of Jupiter’s Moons
Each Galilean moon presents unique geological features. Europa’s icy crust, Ganymede’s magnetic anomalies, Io’s volcanic activity, and Callisto’s cratered surface are all areas of intense study. These moons provide valuable insights into planetary formation and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Space Missions to Jupiter
Humanity’s curiosity about Jupiter has led to numerous space missions aimed at unraveling its mysteries.
History of Jupiter Exploration
The journey to understand Jupiter began with Pioneer and Voyager missions in the 1970s. These early missions provided the first close-up images of the giant planet and its moons.
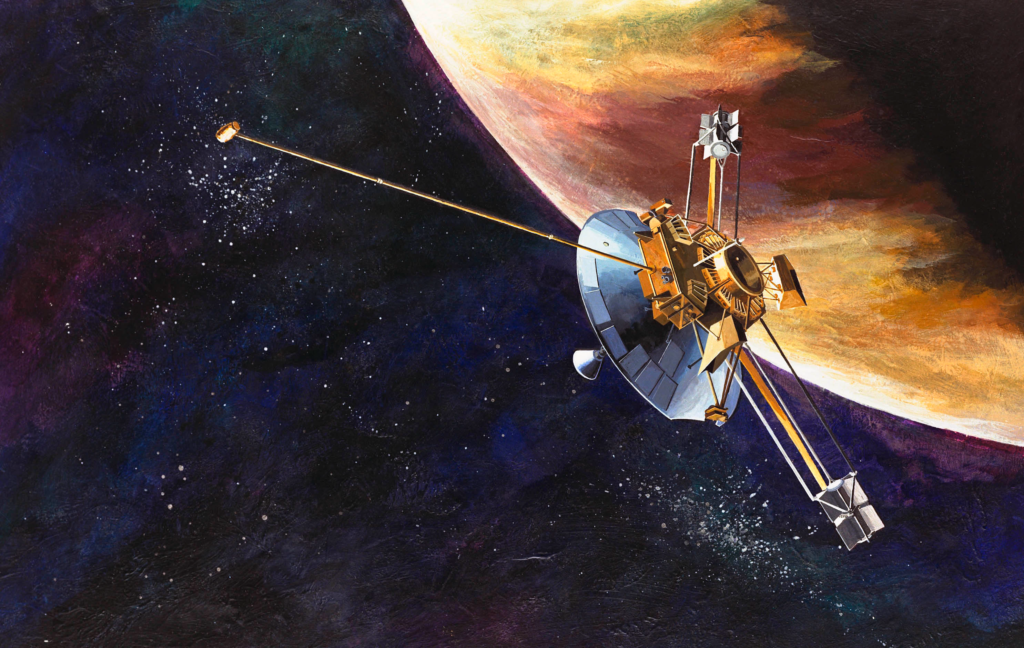
Pioneer and Voyager Missions
The Pioneer 10 and 11 missions were the first to fly by Jupiter, sending back valuable data about its atmosphere and magnetosphere. The Voyager 1 and 2 missions followed, capturing detailed images of the planet and its moons.
Galileo Spacecraft and its Discoveries
The Galileo spacecraft, launched in 1989, was the first to orbit Jupiter. Over its eight-year mission, Galileo made groundbreaking discoveries, including evidence of subsurface oceans on Europa and intense volcanic activity on Io.
Juno Mission: Objectives and Findings
Currently, the Juno mission is providing new insights into Jupiter’s atmosphere, magnetic field, and interior structure. Launched in 2011, Juno’s close flybys have revealed unprecedented details about the planet’s weather patterns and magnetic anomalies.
Future Missions to Jupiter and its Moons
Looking ahead, missions like the Europa Clipper aim to further explore Europa’s potential habitability. These future missions will continue to expand our understanding of Jupiter and its diverse system of moons.
Jupiter’s Influence on the Solar System
Jupiter’s massive size and gravity have a significant impact on the entire Solar System.
Jupiter’s Gravitational Effects
Jupiter’s gravity affects the orbits of many objects, including asteroids and comets. It acts as a cosmic vacuum cleaner, pulling in or deflecting potentially hazardous objects that might otherwise threaten the inner planets.
Interaction with Asteroids and Comets
The Trojan asteroids are a group of asteroids that share Jupiter’s orbit. These asteroids provide clues about the early Solar System. Additionally, Jupiter’s gravity can capture comets, drawing them into new orbits or sending them on a one-way trip into the Sun.
Jupiter’s Role in Protecting Inner Planets
By diverting or capturing dangerous objects, Jupiter helps protect the inner planets, including Earth, from frequent impacts. This protective role underscores its importance in the architecture of our Solar System.
Influence on Solar System Formation
Jupiter’s formation and migration played a crucial role in shaping the Solar System. Its immense gravity likely influenced the formation and arrangement of other planets, as well as the distribution of asteroids and comets.
Jupiter’s Atmospheric Phenomena
Jupiter’s atmosphere is a dynamic and ever-changing environment.
Dynamics of Jupiter’s Atmosphere
The planet’s atmosphere is characterized by strong winds and rapid rotation. These factors contribute to the formation of complex weather patterns, including massive storms and persistent high-speed jet streams.
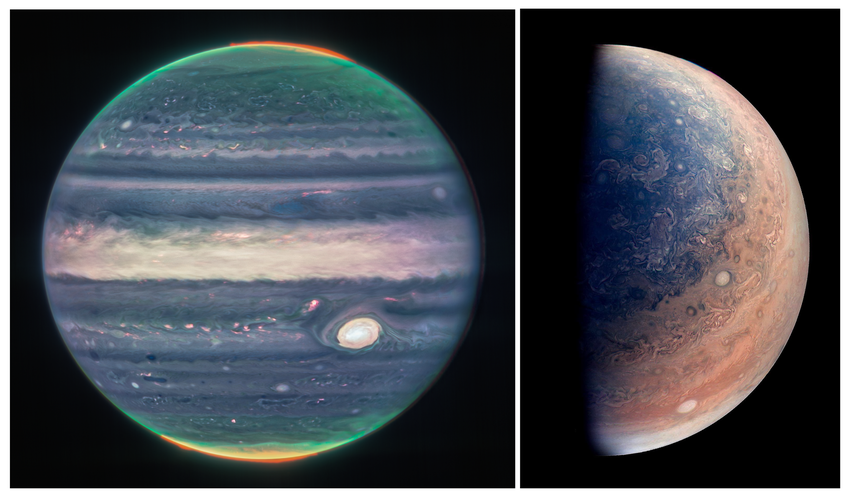

Understanding the Great Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is a high-pressure storm that has persisted for centuries. Recent observations suggest it may be shrinking, but it remains a key feature in understanding Jupiter’s atmospheric dynamics.
Other Storms and Weather Patterns
Jupiter’s atmosphere hosts numerous other storms, including white ovals and brown barges. These features, along with the planet’s bands and zones, provide a laboratory for studying meteorology on a grand scale.
Auroras and Atmospheric Emissions
Jupiter’s strong magnetic field generates intense auroras at its poles. These auroras are not only visually stunning but also provide information about the planet’s magnetosphere and the interaction between the solar wind and Jupiter’s atmosphere.
The Importance of Studying Jupiter
Studying Jupiter offers numerous scientific and practical benefits.
Insights into Planetary Formation
Jupiter’s composition and structure provide clues about the early Solar System and the processes that led to the formation of planets. Understanding Jupiter helps us learn more about how other planetary systems might form.
Understanding Gas Giants in Other Solar Systems
Jupiter serves as a model for gas giants found in other star systems. By studying Jupiter, scientists can infer the characteristics and behavior of exoplanets, enhancing our knowledge of the universe.
Contributions to Astronomy and Astrophysics
Research on Jupiter contributes to broader fields of astronomy and astrophysics. From understanding planetary atmospheres to studying magnetic fields, Jupiter’s study has far-reaching implications.
Technological Advancements from Jupiter Missions
Missions to Jupiter have driven technological innovations, from spacecraft design to advanced scientific instruments. These advancements have applications beyond space exploration, benefiting various industries.
Challenges of Exploring Jupiter
Exploring Jupiter poses significant challenges that must be overcome.
Harsh Radiation Belts
Jupiter’s radiation belts are incredibly intense, posing a hazard to spacecraft and instruments. Designing technology that can withstand this harsh environment is a major challenge.
Extreme Atmospheric Conditions
The planet’s thick atmosphere and high-pressure conditions make direct exploration difficult. Understanding and preparing for these conditions is essential for future missions.
Technological and Engineering Challenges
Sending spacecraft to Jupiter requires advanced engineering and innovative solutions. From long-duration missions to deep space communication, the technical challenges are immense.
Overcoming Obstacles in Future Missions
Future missions to Jupiter must address these challenges to succeed. Continued research and development are crucial for overcoming the obstacles posed by Jupiter’s extreme environment.
Jupiter in Culture and Mythology
Jupiter has held a place of significance in human culture and mythology for millennia.
Historical Significance of Jupiter
Ancient civilizations observed Jupiter and incorporated it into their understanding of the cosmos. Its consistent presence in the night sky made it a focal point for early astronomers.
Jupiter in Roman Mythology
In Roman mythology, Jupiter was the king of the gods, wielding thunderbolts and presiding over the heavens. This mythological heritage reflects the planet’s dominance in the sky.
Influence on Modern Culture
Jupiter continues to inspire modern culture, appearing in literature, movies, and art. Its majestic appearance and intriguing moons captivate the imagination.

Depictions in Literature and Media
From science fiction novels to blockbuster films, Jupiter often features in stories about space exploration and the mysteries of the universe. These depictions highlight the planet’s enduring allure.
By exploring these aspects of Jupiter, we gain a deeper understanding of not only the planet itself but also its role in our Solar System and its significance in human culture. This knowledge enriches our appreciation of the cosmos and fuels our curiosity about the universe beyond.
Is Jupiter A Brown Dwarf?
Jupiter is not a brown dwarf. Although brown dwarfs share some characteristics with gas giants like Jupiter, such as being composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, they are significantly larger and capable of initiating some fusion reactions. Jupiter, however, lacks the mass required to sustain fusion, which is a defining characteristic of brown dwarfs. Brown dwarfs typically have masses between 13 and 80 times that of Jupiter (Little Astronomy) (Wikipedia).
Who Discovered Jupiter?
Jupiter has been known since ancient times and can be seen with the naked eye. Therefore, it doesn’t have a single discoverer. Ancient civilizations such as the Greeks and Romans observed and named the planet. The Greeks named it after their god Zeus, and the Romans later adopted the name Jupiter, after their chief god (Little Astronomy) (Wikipedia).
How Big is Jupiter?
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, with a radius of approximately 69,911 kilometers (43,441 miles). This makes it nearly 11 times wider than Earth. The volume of Jupiter is so vast that it could contain over 1,300 Earths. Its immense size and mass significantly influence the solar system’s dynamics (NASA Space Place) (Wikipedia).
Does Jupiter Have Water?
Yes, Jupiter contains water, but not in the form of oceans or lakes. Water on Jupiter exists as vapor in its atmosphere. The water vapor makes up about 0.25% of the molecules in Jupiter’s atmosphere, which, considering the planet’s size, amounts to a significant volume (Little Astronomy) (Wikipedia).
Why Does Jupiter Have So Many Moons?
Jupiter has a vast number of moons due to its strong gravitational pull, which allows it to capture and hold onto a large number of natural satellites. As of now, Jupiter has 95 known moons, including the four large Galilean moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. These moons vary greatly in size and composition, with some, like Ganymede, being larger than the planet Mercury (Little Astronomy) (NASA Space Place) (Wikipedia).
So, there you have it! Jupiter is a fascinating planet with many amazing features, from its massive size to its stormy atmosphere and intriguing moons. Space missions continue to reveal more secrets about this gas giant. Want to learn more or share your thoughts? Leave a comment, share this article, or check out more content on galaxysecrets. Happy stargazing!








