Do you ever wonder how rockets fly to space? It’s amazing and not too hard to understand. Rockets work by shooting gas out and going the opposite way. We’ll learn how rockets work, their history, and who makes them. We’ll see what they do now and what cool new things they can do soon.
Stay with us, and we’ll dive into the basics of rocket engines, the stages of their flights, and companies like NASA and SpaceX making big moves in space.
Basic Principles of Rocket Propulsion
Rockets operate on a straightforward yet powerful principle: Newton’s Third Law of Motion. For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In simpler terms, rockets expel gas out of the engine, and this action propels the rocket forward. The expelled gas is typically produced by burning rocket fuel, which comes in various types, each suited for different purposes.
Types of Rocket Engines
Rocket engines come in different forms, mainly liquid and solid fuel engines. Liquid-fueled rockets, like those used by SpaceX’s Falcon 9, utilize a combination of liquid oxygen and kerosene, which are mixed and ignited to produce thrust. On the other hand, solid-fueled rockets use a solid propellant that burns to create the necessary thrust. Each type has its own advantages and applications in space exploration.
Rocket Fuel Types and Their Uses
The choice of rocket fuel depends on the mission requirements. Common types include:
- Liquid hydrogen and oxygen: Used in many space missions due to its efficiency and high thrust-to-weight ratio.
- RP-1 (Refined Kerosene): A favorite for many modern rockets, such as those from SpaceX.
- Solid propellants: Often used in military missiles and some space missions for their simplicity and reliability.
Stages of Rocket Launch and Flight
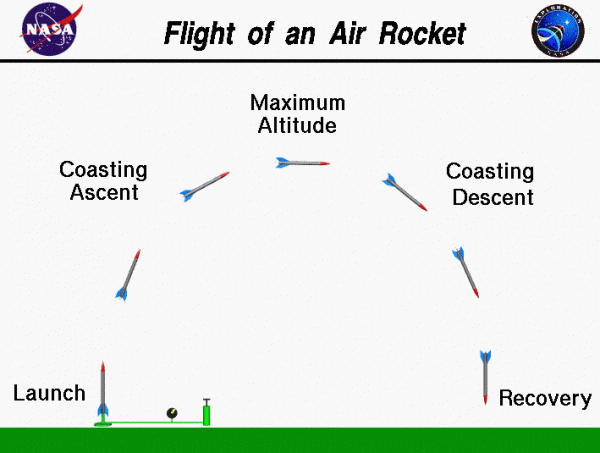
Rocket launches are a marvel of engineering, involving multiple stages to reach their destination. A typical rocket launch sequence includes:
- Liftoff: The rocket engines ignite, producing thrust to overcome Earth’s gravity.
- Stage separation: Rockets often have multiple stages, each containing its own engines and fuel. Once a stage’s fuel is depleted, it is jettisoned to lighten the rocket.
- Orbital insertion: The final stage fires to place the rocket into the desired orbit or trajectory.
History and Evolution of Rockets
Early Developments in Rocket Technology
Rocket technology has a long history, dating back to ancient China, where gunpowder was used in simple rockets. These early rockets were more akin to fireworks than the sophisticated space vehicles we have today.
Key Milestones in Rocket History
The journey from those early rockets to modern space exploration has been marked by significant milestones. The Space Race of the mid-20th century, driven by the USA and the Soviet Union, spurred rapid advancements. The launch of Sputnik by the Soviet Union in 1957 and the subsequent Apollo missions by NASA in the 1960s and 70s are notable examples.
The Space Race and Its Impact on Rocket Development
The Space Race led to remarkable achievements in rocket technology. NASA and the Soviet space agency Roscosmos developed powerful rockets capable of reaching the Moon. These efforts not only pushed technological boundaries but also ignited a passion for space exploration worldwide.
Modern Advances in Rocket Technology

Today, companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin are pioneering new technologies. Reusable rockets, such as the Falcon 9 and New Shepard, promise to reduce the cost of space travel, making it more accessible.
Major Rocket Manufacturers and Space Agencies
NASA’s Contributions to Rocket Science
NASA has been at the forefront of rocket science for decades. From the Saturn V that took humans to the Moon to the upcoming Artemis missions, NASA continues to push the envelope.
SpaceX and Its Innovations
SpaceX, founded by Elon Musk, has revolutionized the industry with its reusable rockets. The Falcon Heavy and the ambitious Starship projects are prime examples of their innovative approach.
Blue Origin and Reusable Rockets
Blue Origin, led by Jeff Bezos, is another key player, focusing on reusable rockets like New Shepard and the upcoming New Glenn.
Contributions of Roscosmos, ESA, and CNSA
- Roscosmos: The Russian space agency has a rich history, from Sputnik to the Soyuz missions.
- ESA (European Space Agency): Known for its Ariane rockets, ESA collaborates with other agencies to further space exploration.
- CNSA (China National Space Administration): A rapidly growing force in space exploration, with notable achievements like the Long March rockets and lunar missions.
Other Key Players in the Rocket Industry
Other significant contributors include Rocket Lab, known for its Electron rocket, and United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture of Boeing and Lockheed Martin.
Current and Upcoming Rocket Missions
Recent Successful Rocket Launches
Recent years have seen numerous successful launches. Notable ones include SpaceX’s Crew Dragon missions to the International Space Station (ISS) and Blue Origin’s suborbital flights.
Scheduled Launches and Missions
Upcoming missions, such as NASA’s Artemis program aiming to return humans to the Moon and SpaceX’s Mars missions, promise exciting developments in space exploration.
Notable Space Missions and Their Objectives
Each mission has unique objectives, from studying distant planets to deploying satellites for global communication. The James Webb Space Telescope, launched by NASA, seeks to unravel the mysteries of the universe.
International Collaboration in Space Exploration
Space agencies worldwide collaborate on missions, pooling resources and expertise. Projects like the ISS are prime examples of what can be achieved through international cooperation.
The Science Behind Rocket Propulsion
Understanding Thrust and Velocity
Thrust is the force that propels a rocket, while velocity determines its speed. Achieving the right balance between these is crucial for a successful mission.
The Role of Multi-Stage Rockets
Multi-stage rockets are designed to shed weight as they ascend, making them more efficient. Each stage ignites sequentially, providing the necessary thrust to reach space.
Innovations in Propellant and Engine Design
Advances in propellant technology and engine design are continuously improving rocket performance. The development of electric propulsion systems is a notable example.
Challenges and Solutions in Rocket Engineering
Rocket engineering faces numerous challenges, from ensuring structural integrity to dealing with extreme temperatures. Innovations in materials and design are key to overcoming these obstacles.
The Future of Rocket Technology

Reusable Rockets and Their Impact
Reusable rockets are changing the landscape of space travel by reducing costs. SpaceX’s Falcon 9 and Blue Origin’s New Shepard are leading examples.
Advancements in Hypersonic Rockets
Hypersonic rockets, capable of traveling at speeds greater than five times the speed of sound, hold promise for faster space travel and defense applications.
The Role of AI and Automation in Rocket Launches
AI and automation are becoming integral in rocket launches, improving precision and safety. Autonomous systems guide rockets from launch to landing.
Potential for Deep Space Exploration
As technology advances, the potential for deep space exploration grows. Missions to Mars and beyond are becoming more feasible, paving the way for future interplanetary travel.
The Impact of Rockets on Society and Economy
Economic Benefits of Rocket Launches
Rocket launches stimulate economic growth by creating jobs and fostering innovation. The space industry generates billions in revenue annually.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
While rockets are essential for space exploration, they also impact the environment. Efforts are underway to develop more sustainable technologies and practices.
Rockets in Popular Culture and Media
Rockets have captured the imagination of people worldwide, appearing in movies, books, and art. They symbolize human curiosity and the drive to explore.
Educational Programs and Public Engagement
Educational programs and public outreach efforts aim to inspire the next generation of scientists and engineers. Events like rocket launches captivate audiences and promote interest in STEM fields.
Rockets and Space Tourism

The Rise of Commercial Space Travel
Commercial space travel is becoming a reality, with companies like SpaceX and Blue Origin leading the charge. Space tourism offers a new frontier for adventure.
Companies Leading the Way in Space Tourism
SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Virgin Galactic are at the forefront of this burgeoning industry, each offering unique experiences for aspiring space tourists.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
While exciting, space tourism faces challenges such as safety, cost, and regulatory hurdles. However, it also presents opportunities for scientific research and technological advancement.
Future Prospects for Space Tourism
As technology improves and costs decrease, space tourism is expected to grow, potentially becoming a mainstream option for travel and exploration.
Conclusion
Rockets are incredible, taking us to new frontiers in space. We’ve looked at how they work, their history, and their exciting future. Rockets help us learn more about the universe and drive new technology. What do you think about rockets? Share your thoughts, and check out more cool space stuff at Galaxy Secrets.
FAQs About Rockets
How does Newton’s third law apply to rockets?
Newton’s third law of motion is fundamental to rocket science. It states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. In the context of rockets, when the engine expels exhaust gases downward, an equal and opposite force propels the rocket upward. This principle is the core reason rockets can launch into space, overcoming Earth’s gravity by producing enough thrust to ascend (Space.com) (NASA).
What are the different types of rocket engines?
Rockets generally use two types of engines: solid-fueled and liquid-fueled. Solid-fueled rockets have a simpler design where the fuel and oxidant are mixed and solidified. Once ignited, they burn until the fuel is exhausted. Liquid-fueled rockets are more complex, involving separate tanks for fuel and oxidant. These components are mixed in a combustion chamber and ignited to produce thrust. Liquid-fueled engines can be throttled, stopped, and restarted, offering greater control during flight (Space.com) (NASA).
How do rockets steer in space?
Rockets steer using several methods. Most commonly, they use gimbaled engines that can pivot to direct thrust. Other methods include using external vanes to deflect the exhaust or auxiliary thruster rockets mounted on the sides. These steering mechanisms are crucial for maintaining the correct trajectory and ensuring the rocket reaches its intended destination (Space.com).








