Supernovae are big star explosions, and they make a huge impact in space. A supernova happens when a star reaches its end.
There are two main types: Type Ia and Type II. In this article, we’ll look at how these explosions happen, their effects on the galaxy, and how scientists study them. You will see why supernovae are so important and how they change everything around them. Let’s explore the wonders of these cosmic events together!
What is a Supernova?
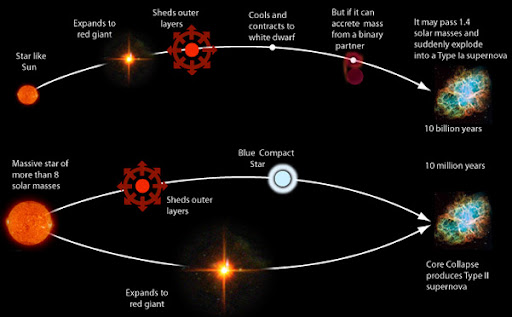
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion that occurs at the end of a star’s lifecycle. There are two main types of supernovae: Type Ia and Type II.
- Type Ia supernovae happen in binary star systems where one star is a white dwarf. When the white dwarf accumulates enough matter from its companion, it triggers a runaway fusion reaction, leading to a supernova.
- Type II supernovae occur when massive stars exhaust their nuclear fuel. This causes the star’s core to collapse under gravity, leading to an explosive outburst.
These explosions are not only breathtaking but also crucial for the universe. They play a significant role in distributing heavy elements like iron and nickel across space, enriching the interstellar medium.

How Do Supernovae Occur?
The process of a supernova begins with stellar evolution. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Stellar Evolution: Stars spend most of their lives fusing hydrogen into helium in their cores. Over time, they evolve into red giants or supergiants, depending on their mass.
- Core Collapse (for Type II): In massive stars, once the core is mostly iron, it can’t support the star against gravitational collapse. The core collapses rapidly, creating a supernova explosion.
- Thermonuclear Explosion (for Type Ia): In binary systems, when a white dwarf gains enough mass, it triggers a thermonuclear explosion that tears the star apart.
These mechanisms ensure that supernovae are among the most energetic and transformative events in the cosmos.
The Impact of Supernovae on the Galaxy
Supernovae have profound effects on their surroundings. They influence:
- Stellar Systems: The explosion can disrupt nearby stars and planetary systems.
- Chemical Enrichment: Supernovae disperse heavy elements into the interstellar medium, contributing to the formation of new stars and planets.
- Interstellar Medium: The shock waves from supernovae compress surrounding gas clouds, which can trigger new star formation.
These processes help shape the structure and composition of galaxies, driving cosmic evolution.
Observing and Studying Supernovae
Observing supernovae involves using advanced telescopes and instruments. Here are some methods:
- Optical Telescopes: These capture visible light from the explosion.
- Radio Telescopes: These detect the radio waves emitted by the expanding supernova remnant.
- X-ray Telescopes: These observe high-energy radiation from the remnants.
Significant discoveries include the observation of supernovae in distant galaxies, which helps scientists understand the rate of cosmic expansion.
Supernova Remnants and Their Importance
After a supernova explosion, the remnants—composed of ejected material—continue to evolve:
- Nebulae Formation: The expelled gas and dust form nebulae, which are the birthplaces of new stars.
- Evolution: Supernova remnants expand and cool over time, contributing to the formation of structures like pulsars and neutron stars.
- Impact: These remnants influence the surrounding space, impacting galactic dynamics and star formation.
The Role of Supernovae in Stellar and Galactic Evolution
Supernovae are integral to both stellar and galactic evolution. They:
- Affect Star Formation Cycles: By compressing nearby gas clouds, they can trigger the formation of new stars.
- Influence Galactic Dynamics: The energy and matter ejected alter the structure and composition of galaxies.

Case Studies of Supernovae in Different Galaxies
Observations of supernovae in various galaxies provide insights into different galactic environments and evolutionary processes. For example:
- Supernovae in the Milky Way: Studies of nearby supernovae help refine models of stellar evolution.
- Distant Galaxies: Observing supernovae in distant galaxies helps measure cosmic expansion rates and understand the universe’s history.
Related Cosmic Phenomena
Supernovae are related to several other cosmic phenomena:
- Gamma-Ray Bursts: These are intense bursts of gamma rays, often associated with supernovae.
- Black Hole Formation: Some supernovae result in the formation of black holes.
- Hypernovae: These are even more powerful than regular supernovae and can lead to gamma-ray bursts.
Conclusion
Supernovae are key to understanding the universe. They enrich space with elements, influence star and galaxy formation, and provide valuable data about cosmic processes. As research continues, we uncover more about these cosmic phenomena, deepening our knowledge of the universe’s vast and dynamic nature.
By exploring supernovae, we gain insights into the life cycles of stars and the evolution of galaxies, enhancing our comprehension of the cosmos.
FAQs About Supernovae
What Causes a Supernova?
A supernova occurs due to two main processes. In a Type II supernova, a massive star’s core collapses under its own gravity when nuclear fusion ceases, leading to an explosion. In a Type Ia supernova, a white dwarf in a binary system accumulates material from its companion star until it reaches a critical mass, triggering a thermonuclear explosion. Both types result in the release of immense energy and heavy elements into space.
How Often Do Supernovae Occur?
Supernovae are relatively rare but significant events. In a galaxy like the Milky Way, a supernova occurs roughly once every 50 years. The frequency can vary depending on the galaxy’s size and star formation rate. Observations of distant galaxies and supernovae help astronomers estimate their occurrence rate in the universe.
What Are the Effects of a Supernova on Its Surroundings?
The effects of a supernova are profound. The explosion disperses heavy elements like iron and nickel into the interstellar medium, enriching it for future star formation. The shock wave from the explosion can trigger the collapse of nearby gas clouds, leading to new star systems. Additionally, supernovae can affect nearby stars and planetary systems.








